- Lumiera
- Posts
- 🔆 Meta vs. The EU AI Code of Practice
🔆 Meta vs. The EU AI Code of Practice
Meta's refusal strategy, Netflix' first GenAI show and heart disease diagnostics improve
🗞️ Issue 80 // ⏱️ Read Time: 7 min
In this week's newsletter
What we're talking about: Meta's strategic decision to reject the EU's voluntary Code of Practice for general-purpose AI models, despite mounting regulatory pressure and potential market consequences.
How it's relevant: As the EU AI Act becomes the world's first comprehensive AI regulation, the responses from major tech companies will set precedents for global AI governance and determine whether voluntary compliance can work alongside mandatory rules.
Why it matters: This standoff reveals the deeper tensions between innovation and regulation, corporate strategy and public interest. Understanding these dynamics helps us grasp what's at stake in the emerging global framework for responsible AI development.
Hello 👋
The battle lines are drawn in Brussels. As the EU pushes forward with implementing the AI Act, Meta's recent refusal to sign the EU's Code of Practice for AI has sparked a debate that goes far beyond legal compliance: It's a fundamental clash over who gets to shape the future of AI governance.
The Regulatory Landscape: Setting the Stage
The European Union's AI Act, now in force, represents the attempt to prevent what regulators call a "race to the bottom" in artificial intelligence development. The legislation aims to ensure AI systems are developed and deployed safely, transparently, and in ways that protect fundamental rights.
However, the path to implementation hasn't been smooth. Major European technology companies, including ASML, SAP, and Mistral AI, along with over 110 other organizations, have formally asked the European Union to delay implementation. In a letter to European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, these business leaders argue that the forthcoming regulations could jeopardize the EU's position in global AI innovation and call for a more "innovation-friendly regulatory approach."
Despite this industry pushback, the European Commission announced that implementation will continue as planned and launched the EU's Code of Practice as a bridge between regulatory requirements and practical compliance.
Understanding the AI Code of Practice
The EU's AI Code of Practice serves as a voluntary framework designed to help companies implement the AI Act's requirements:
It requires companies to provide comprehensive documentation about their AI tools, including how models are trained, what data is used, and how risks are managed.
Crucially, it bans training AI on pirated content and requires compliance with content owners' requests to exclude their works from datasets.
The code aims to create industry standards that promote transparency, accountability, and responsible innovation while building public trust in AI systems.
For society, it promises greater transparency and protection from potentially harmful AI systems.
Meta's Public Position: The Official Reasons
Meta's refusal to sign the GPAI came through Joel Kaplan, the company's Chief Global Affairs Officer, in a LinkedIn post that sent ripples through the tech industry.
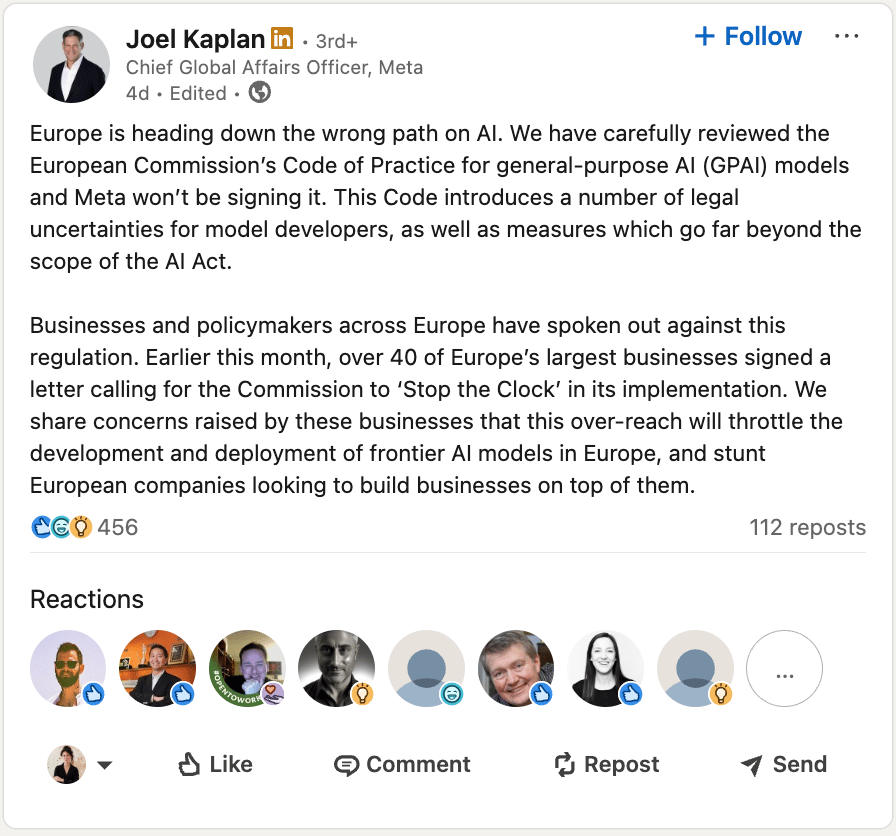
Kaplan outlines three primary objections. Let’s take a closer look at what it actually means.
Legal Uncertainty: Meta argues the code introduces numerous legal uncertainties, claiming requirements are vaguely defined and could expose them to unexpected legal risks.
Regulatory Overreach: The company claims the code includes "measures which go far beyond the scope of the AI Act," suggesting regulators are using the voluntary framework to impose requirements not explicitly mandated in the original legislation.
Innovation Concerns: Meta echoes the broader industry concern that "this over-reach will throttle the development and deployment of frontier AI models in Europe."
The False Dichotomy: Why the “Regulation Kills Innovation" Argument Doesn't Hold Up
Meta's resistance relies heavily on a familiar industry talking point: that regulation inherently stifles innovation. This narrative, while seductive in its simplicity, represents a false dichotomy that obscures a far more nuanced reality.
The Standard Industry Playbook
The "regulation hates innovation" argument follows a predictable pattern:
Companies claim compliance costs divert resources from R&D,
Regulatory uncertainty makes long-term planning impossible, and
Restrictive rules limit technological exploration.
This framing positions companies as champions of progress fighting bureaucratic obstacles while casting regulators as risk-averse bureaucrats who don't understand technology.
The Research Tells a Different Story
However, decades of research reveal that well-designed regulation can actually foster innovation by setting clear goals that act as "demand signals," building public trust essential for adoption, preventing races to the bottom, and spurring compliance-driven innovation. For example, The Montreal Protocol banning ozone-depleting substances spurred innovation in refrigeration and aerosol technologies, creating entirely new chemical industries
Why Companies Keep Using This Argument
Companies continue deploying this argument because regulation creates immediate, visible compliance costs while innovation benefits emerge over longer time horizons. Additionally, early compliance can disadvantage first-movers compared to competitors who delay, creating incentives to resist collectively rather than compete on responsibility.
Beyond the "regulation kills innovation" narrative, what other false dichotomies do you encounter in discussions about technology policy or business strategy? How might more nuanced thinking change these debates?
Understanding the Strategic Calculations
Meta's resistance reveals calculations extending far beyond immediate compliance requirements. The company's business model depends on maximizing scale and speed to market with minimal oversight. The code's documentation and transparency requirements create friction that could slow development and potentially reveal competitive advantages.
Meta appears to be testing EU enforcement limits while negotiating from a position of strength. By aligning with other dissenting voices, Meta is betting Brussels might soften requirements to avoid losing major tech players.
However, this approach creates fundamental misalignment with market dynamics. Meta's resistance comes when the company already faces significant trust deficits from scandals like Cambridge Analytica. The EU framework offers a pathway to rebuild public confidence through documented responsible practices, yet Meta is rejecting this opportunity. This creates strategic openings for competitors willing to embrace transparency as a competitive differentiator, which is particularly important as users increasingly demand responsible AI development and enterprise customers require compliance capabilities.
What This Means for the Future
Meta's strategic resistance represents more than a single company's regulatory gambit, it's a test case for how global AI governance will evolve. The outcome will influence whether voluntary compliance mechanisms can work alongside mandatory regulations.
If other major tech companies follow Meta's lead, it could undermine the EU's attempt to establish Europe as a global standard-setter for responsible AI. Conversely, if market pressures eventually force Meta to participate, it could cement the Brussels Effect in AI governance, where EU regulations become de facto global standards.
Big tech news of the week…
🎥 Netflix used generative AI in one of its shows for the first time, which allowed them to fund the show at a much lower cost than is typical for a big-budget production.
🌟 Companies recognize that higher-quality, expertly labeled data is crucial for developing more accurate and reliable AI systems. Leading artificial intelligence groups are moving away from relying on low-cost, gig-economy data labellers based in Africa and Asia, opting instead to hire highly paid industry specialists to handle the increasingly complex work of data annotation.
♥️ Recent advances in machine learning applied to heart rhythm recordings have shown promise in identifying structural heart disease, a growing epidemic that remains substantially underdiagnosed
📱 AI privacy startup Confident Security emerges from stealth mode with an end-to-end encryption tool that wraps around foundational models, guaranteeing that prompts and metadata can’t be stored, seen, or used for AI training, even by the model provider or any third party.
Until next time.
On behalf of Team Lumiera
Lumiera has gathered the brightest people from the technology and policy sectors to give you top-quality advice so you can navigate the new AI Era.
Follow the carefully curated Lumiera podcast playlist to stay informed and challenged on all things AI.

Disclaimer: Lumiera is not a registered investment, legal, or tax advisor, or a broker/dealer. All investment/financial opinions expressed by Lumiera and its authors are for informational purposes only, and do not constitute or imply an endorsement of any third party's products or services. Information was obtained from third-party sources, which we believe to be reliable but not guaranteed for accuracy or completeness. |